AI-Based Network Attack Classification System


📌 Project Overview
Traditional rule-based security systems often struggle to detect novel or mutating cyber threats. To address this limitation, I developed an AI-powered classification system capable of identifying various attack patterns dynamically.
This project utilizes machine learning algorithms to analyze network payloads and classify them into specific threat categories, achieving an overall accuracy of 92.6%.
📊 Dataset & Features
The model was trained on a dataset containing 220,000 network traffic entries.
Target Classes (Attack Types)
- Normal: Legitimate traffic
- Brute Force: Automated password guessing attacks
- SQL Injection (SQLi): Malicious SQL queries
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Script injection attacks
- System Cmd Execution: Unauthorized shell command execution
🛠️ Feature Engineering (Preprocessing)
Raw payload data cannot be directly fed into ML models. I implemented a custom preprocessing pipeline to extract meaningful features from the text payload:
- Method Extraction: Separated HTTP methods (GET, POST).
- Keyword Flagging: Created binary features for common attack tools and patterns found in payloads:
sqlmap,hydra(Attack tools)arachni,zap(Scanners)userid,cmd(Suspicious parameters)
# Example Preprocessing Code
def prepro(data):
data['method'] = data['payload'].str.split().str[0].map({'POST':0, 'GET':1})
data['sql'] = data['payload'].apply(lambda x: 1 if 'sqlmap' in x.lower() else 0)
data['word'] = data['payload'].apply(add_word) # Custom function for keyword groups
# ... (additional feature extraction)
return data[['method', 'sql', 'word', ...]]
🤖 Model Development & Evaluation
I trained and compared three different classification models to find the best performer: **1. Random Forest Classifier
- Logistic Regression
- XGBoost**
Results Random Forest demonstrated the best performance with stable detection rates across major attack types.
- Overall Accuracy: 92.6%
- Brute Force F1-Score: 0.99 (Near perfect detection)
- SQL Injection F1-Score: 0.93
Classification Report (Random Forest):
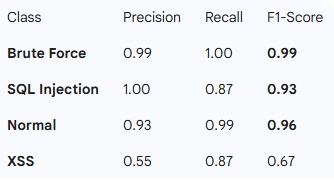
(Note: While Brute Force and SQLi detection were excellent, XSS and System Cmd Execution showed room for improvement, highlighting areas for future feature engineering.)
Feature Importance Analysis
Using the Random Forest model, I analyzed which features contributed most to detection.
- ‘word’ feature (Tool Signatures): Highest importance. This indicates that attack tool signatures (e.g., Hydra, Sqlmap) are critical indicators.
- ‘method’ (GET/POST): Significant for distinguishing payload types.
🎯 Conclusion
This project successfully demonstrated that machine learning can automate the classification of network attacks with high accuracy. By shifting from static rules to dynamic feature learning, the system can more effectively handle high-volume traffic and aid security analysts in rapid triage.
Future Improvements:
- Implementing Deep Learning (RNN/LSTM) to better understand payload sequences for improving XSS detection.
- Deploying the model as a real-time API service.
